(1). 先看下TMClient类的结构图
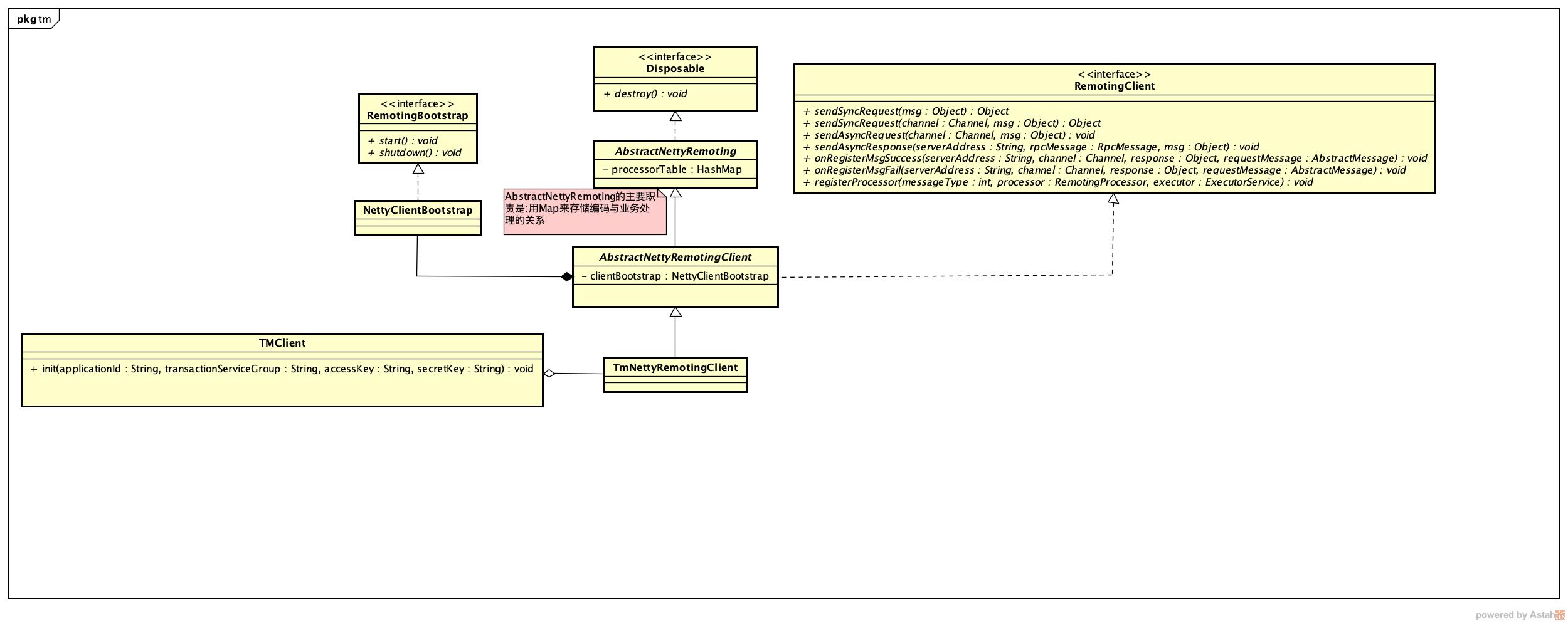
TM全称为:Transaction Manager,它的作用是向TC(事务协调器),注册全局事务.
从类(RemotingClient)图上能看出,它的大体职责:同步发送消息/异步发送消息/注册消息处理器…
(2). TMClient.init
public static void init(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup, String accessKey, String secretKey) {
// 3. 典型的单例模式: TmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance
TmNettyRemotingClient tmNettyRemotingClient = TmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance(applicationId, transactionServiceGroup, accessKey, secretKey);
// ... ...
}
(3). TmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance
public static TmNettyRemotingClient getInstance(String applicationId, String transactionServiceGroup, String accessKey, String secretKey) {
// 4. getInstance
// 双重加锁机制创建:TmNettyRemotingClient,然后,设置属性值
TmNettyRemotingClient tmRpcClient = getInstance();
// ... ...
return tmRpcClient;
}
(4). TmNettyRemotingClient.getInstance
public static TmNettyRemotingClient getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
synchronized (TmNettyRemotingClient.class) {
if (instance == null) {
// 创建配置信息类
NettyClientConfig nettyClientConfig = new NettyClientConfig();
// 创建线程池执行器
final ThreadPoolExecutor messageExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
nettyClientConfig.getClientWorkerThreads(), nettyClientConfig.getClientWorkerThreads(),
KEEP_ALIVE_TIME, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(MAX_QUEUE_SIZE),
new NamedThreadFactory(nettyClientConfig.getTmDispatchThreadPrefix(),
nettyClientConfig.getClientWorkerThreads()),
RejectedPolicies.runsOldestTaskPolicy());
// **************************************************************
// 5. 构造:TmNettyRemotingClient
// **************************************************************
instance = new TmNettyRemotingClient(nettyClientConfig, null, messageExecutor);
}
}
}
return instance;
} // end getInstance
(5). TmNettyRemotingClient
private TmNettyRemotingClient(NettyClientConfig nettyClientConfig,
EventExecutorGroup eventExecutorGroup,
ThreadPoolExecutor messageExecutor) {
// 6. 调用父类的构造器(AbstractNettyRemotingClient)
super(nettyClientConfig, eventExecutorGroup, messageExecutor, NettyPoolKey.TransactionRole.TMROLE);
// 通过SPI加载AuthSigner(在与TC通信时,用于数据签名处理)
this.signer = EnhancedServiceLoader.load(AuthSigner.class);
}
(6). AbstractNettyRemotingClient
public AbstractNettyRemotingClient(NettyClientConfig nettyClientConfig, EventExecutorGroup eventExecutorGroup,
ThreadPoolExecutor messageExecutor, NettyPoolKey.TransactionRole transactionRole) {
super(messageExecutor);
this.transactionRole = transactionRole;
// ************************************************************
// 在这里创建了:Bootstrap的包装类
// ************************************************************
clientBootstrap = new NettyClientBootstrap(nettyClientConfig, eventExecutorGroup, transactionRole);
// ************************************************************
// 设置Netty接受请求后的Handler实现类
// ************************************************************
clientBootstrap.setChannelHandlers(new ClientHandler());
clientChannelManager = new NettyClientChannelManager(
new NettyPoolableFactory(this, clientBootstrap), getPoolKeyFunction(), nettyClientConfig);
}
(7). AbstractNettyRemotingClient$ClientHandler
@Sharable
class ClientHandler extends ChannelDuplexHandler {
@Override
public void channelRead(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
// 消息解码后,如果不是指定类型的消息,则忽略
if (!(msg instanceof RpcMessage)) {
return;
}
// 对消息进行分发
processMessage(ctx, (RpcMessage) msg);
}
// ... ...
}
(8). AbstractNettyRemoting.processMessage
//domain
// 消息类型与业务处理的关联映射
protected final HashMap<Integer/*MessageType*/, Pair<RemotingProcessor, ExecutorService>> processorTable = new HashMap<>(32);
// seata提供了相应的hook,允许用户订阅,并回调
protected final List<RpcHook> rpcHooks = EnhancedServiceLoader.loadAll(RpcHook.class);
// methods
protected void processMessage(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcMessage rpcMessage) throws Exception {
// ... ...
Object body = rpcMessage.getBody();
if (body instanceof MessageTypeAware) {
MessageTypeAware messageTypeAware = (MessageTypeAware) body;
// *******************************************************
// 根据编码(key),获得value(Pair<RemotingProcessor, ExecutorService>)
// *******************************************************
final Pair<RemotingProcessor, ExecutorService> pair = this.processorTable.get((int) messageTypeAware.getTypeCode());
if (pair != null) {
// 首先交给:second处理
if (pair.getSecond() != null) {
try {
// 获得线程池对象,提交任务
pair.getSecond().execute(() -> {
try {
pair.getFirst().process(ctx, rpcMessage);
} catch (Throwable th) {
LOGGER.error(FrameworkErrorCode.NetDispatch.getErrCode(), th.getMessage(), th);
}
});
} catch (RejectedExecutionException e) {
LOGGER.error(FrameworkErrorCode.ThreadPoolFull.getErrCode(),
"thread pool is full, current max pool size is " + messageExecutor.getActiveCount());
if (allowDumpStack) { // defautl allowDumpStack
// ******************************************
// 打dump
// ******************************************
String name = ManagementFactory.getRuntimeMXBean().getName();
String pid = name.split("@")[0];
int idx = new Random().nextInt(100);
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("jstack " + pid + " >d:/" + idx + ".log");
} catch (IOException exx) {
LOGGER.error(exx.getMessage());
}
allowDumpStack = false;
}
}
} else {
try {
// 如果second不存的情况下,交给first处理
pair.getFirst().process(ctx, rpcMessage);
} catch (Throwable th) {
LOGGER.error(FrameworkErrorCode.NetDispatch.getErrCode(), th.getMessage(), th);
}
}
} else {
LOGGER.error("This message type [{}] has no processor.", messageTypeAware.getTypeCode());
}
} else {
LOGGER.error("This rpcMessage body[{}] is not MessageTypeAware type.", body);
}
} //end processMessage
// 注册请求编码与相应的RemotingProcessor
public void registerProcessor(int requestCode, RemotingProcessor processor, ExecutorService executor) {
Pair<RemotingProcessor, ExecutorService> pair = new Pair<>(processor, executor);
this.processorTable.put(requestCode, pair);
}
(9). TmNettyRemotingClient.registerProcessor
查看TmNettyRemotingClient注册了哪些:RemotingProcessor
private void registerProcessor() {
// 1.registry TC response processor
ClientOnResponseProcessor onResponseProcessor =
new ClientOnResponseProcessor(mergeMsgMap, super.getFutures(), getTransactionMessageHandler());
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_SEATA_MERGE_RESULT, onResponseProcessor, null);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_GLOBAL_BEGIN_RESULT, onResponseProcessor, null);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_GLOBAL_COMMIT_RESULT, onResponseProcessor, null);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_GLOBAL_REPORT_RESULT, onResponseProcessor, null);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_GLOBAL_ROLLBACK_RESULT, onResponseProcessor, null);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_GLOBAL_STATUS_RESULT, onResponseProcessor, null);
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_REG_CLT_RESULT, onResponseProcessor, null);
// 2.registry heartbeat message processor
ClientHeartbeatProcessor clientHeartbeatProcessor = new ClientHeartbeatProcessor();
super.registerProcessor(MessageType.TYPE_HEARTBEAT_MSG, clientHeartbeatProcessor, null);
}
(10). AbstractNettyRemoting.sendSync
看下发送逻辑是怎么做的?
// domain
protected final ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, MessageFuture> futures = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
// methods
protected Object sendSync(Channel channel, RpcMessage rpcMessage, long timeoutMillis) throws TimeoutException {
// ... ...
// 1. 创建消费的返回结果包裹对象(MessageFuture)
MessageFuture messageFuture = new MessageFuture();
messageFuture.setRequestMessage(rpcMessage);
messageFuture.setTimeout(timeoutMillis);
// ****************************************************
// 2. 把消息ID和返回包裹对象(MessageFuture)存入到map中
// ****************************************************
futures.put(rpcMessage.getId(), messageFuture);
// 3. 检查Channel
channelWritableCheck(channel, rpcMessage.getBody());
String remoteAddr = ChannelUtil.getAddressFromChannel(channel);
// 4. 发送之前的钩子函数
doBeforeRpcHooks(remoteAddr, rpcMessage);
// 5. 往channel通道写数据,并监听处理结果
channel.writeAndFlush(rpcMessage).addListener((ChannelFutureListener) future -> {
if (!future.isSuccess()) { // 不成功的情况下
// ****************************************************
// 写出消息成功之后,从map中messageId
// ****************************************************
MessageFuture messageFuture1 = futures.remove(rpcMessage.getId());
if (messageFuture1 != null) {
// 设置返回结果为异常信息
messageFuture1.setResultMessage(future.cause());
}
// 销毁连接
destroyChannel(future.channel());
}
});
try {
// 6. 阻塞(timeoutMillis)毫秒,从messageFuture中获得消息
Object result = messageFuture.get(timeoutMillis, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// 7. 发送之后的钩子函数
doAfterRpcHooks(remoteAddr, rpcMessage, result);
// 8. 返回结果
return result;
} catch (Exception exx) {
LOGGER.error("wait response error:{},ip:{},request:{}", exx.getMessage(), channel.remoteAddress(),
rpcMessage.getBody());
if (exx instanceof TimeoutException) {
throw (TimeoutException) exx;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException(exx);
}
}
}
(11). ClientOnResponseProcessor.process
看一下接受逻辑是怎么做的?
public void process(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcMessage rpcMessage) throws Exception {
// 批量消息处理
if (rpcMessage.getBody() instanceof MergeResultMessage) {
MergeResultMessage results = (MergeResultMessage) rpcMessage.getBody();
// 从合并返回消息中移除消息ID
MergedWarpMessage mergeMessage = (MergedWarpMessage) mergeMsgMap.remove(rpcMessage.getId());
// 以下逻辑是:
// 因为发送消息时,是把:MessageFuture存入到:futures(key:messageid,value = MessageFuture)
// 所以,返回消息时,根据messageid找到:MessageFuture并赋值
for (int i = 0; i < mergeMessage.msgs.size(); i++) {
int msgId = mergeMessage.msgIds.get(i);
MessageFuture future = futures.remove(msgId);
if (future == null) {
if (LOGGER.isInfoEnabled()) {
LOGGER.info("msg: {} is not found in futures.", msgId);
}
} else {
future.setResultMessage(results.getMsgs()[i]);
}
}
} else {
// 非批量消息处理.同上面的逻辑差不多.
MessageFuture messageFuture = futures.remove(rpcMessage.getId());
if (messageFuture != null) {
messageFuture.setResultMessage(rpcMessage.getBody());
} else {
if (rpcMessage.getBody() instanceof AbstractResultMessage) {
if (transactionMessageHandler != null) {
transactionMessageHandler.onResponse((AbstractResultMessage) rpcMessage.getBody(), null);
}
}
}
}
}
(12). 总结
TmNettyRemotingClient主要负责与TC(事务协调器进行通信).主要职责为:
- 向TC注册全局事务.
- 告之TC全局事务的commit或rollback.
- 注意:它不参与分支事务的commit或rollback.
